Wireshark

Having a solid foundation in Networking is essential to becoming a good penetration tester.
Wireshark is the world’s best network analyzer tool. It is an open-source software that enables you to inspect real-time data on a live network.
Wireshark can dissect packets of data into frames and segments giving you detailed information about the bits and bytes in a packet. Wireshark supports all major network protocols and media types. Wireshark can also be used as a packet sniffing tool if you are in a public network. Wireshark will have access to the entire network connected to a router.

Sites like Facebook and Twitter are encrypted now, thanks to https. This means that even though you can capture packets from a victim computer in transit to Facebook, those packets will be encrypted. Still, being able to capture data packets in realtime is an important utility for a penetration tester.
Nmap
Nmap is the first tool you will come across when you begin your career as a penetration tester. Nmap is a fantastic network scanning tool that can give you detailed information about a target. This includes open ports, services, and the operating system running on the victim’s computer.
Nmap is popular among penetration testers for many reasons. It is simple, flexible, and extensible. It offers a simple command-line interface where you can add a few flags to choose different types of scans. Nmap offers simple ping scans to aggressive scans that provide detailed ports and service information.
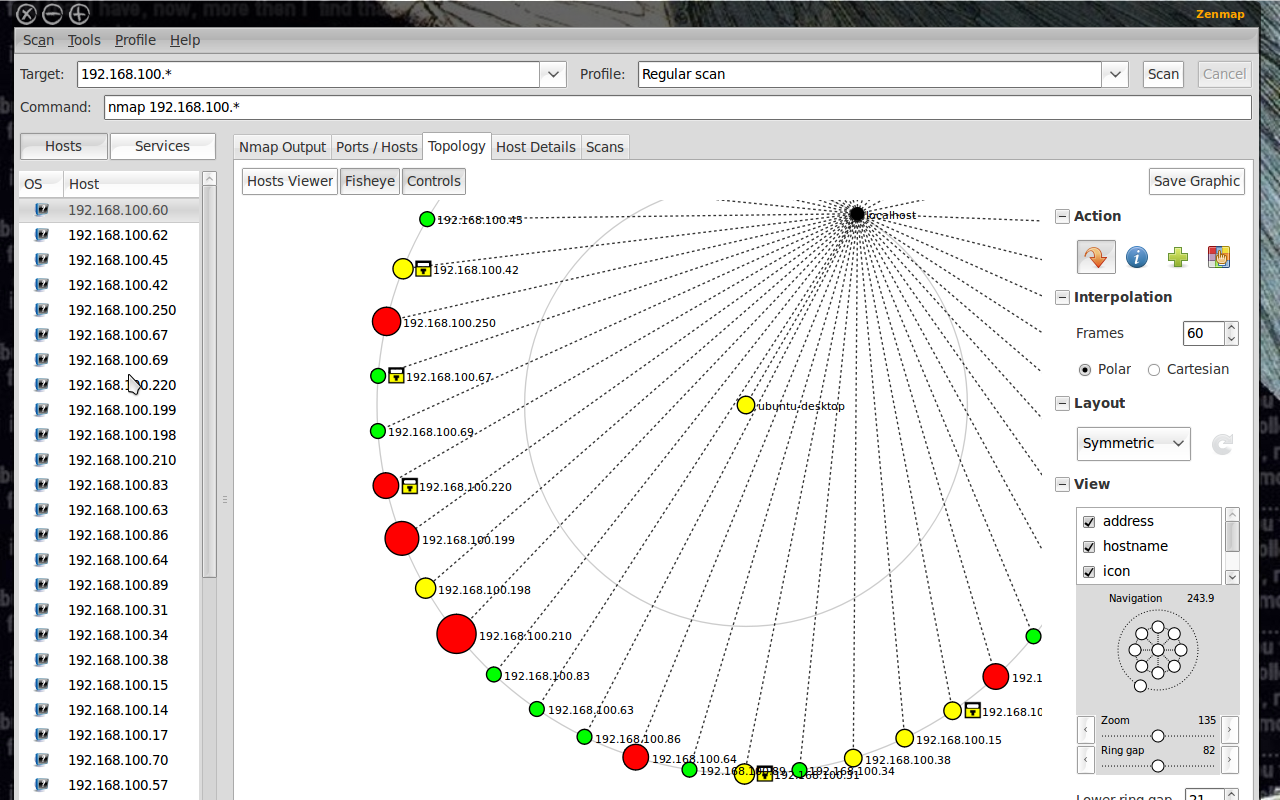
Zenmap UI
Nmap also provides a GUI tool called Zenmap with added utilities. You can build visual network maps and choose scans via dropdowns. Zenmap is a great place to start playing with Nmap commands if you are a beginner.
Metasploit

Metasploit is not just a tool, but a complete framework that you can use during an entire penetration testing lifecycle.
Metasploit contains exploits for most of the vulnerabilities in the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposure database. Using Metasploit, you can send payloads to the target system and gain access to it through a command-line interface.
Metasploit is very advanced with the ability to do tasks such as port scanning, enumeration, and scripting in addition to exploitation. You can also build and test your own exploit using the Ruby programming language.
Metasploit was open-source till 2009 after which Rapid7 acquired the product. You can still access free community edition for free and use all its features.

Nessus

A popular enterprise vulnerability scanner. Nessus is built to be a complete vulnerability analysis and reporting tool. While you can scan and find ports or services using Nmap, Nessus will tell you the list of vulnerabilities and how they can be exploited.
Nessus has an excellent user interface, tens of thousands of plugins, and supports embedded scripting. Nessus is favored by enterprises since it helps companies audit for various compliances like PCI and HIPPA. Nessus will also tell you the severity of the vulnerabilities so that you can focus on those threats accordingly.

Nessus is not a free software but offers a limited free home edition. Nessus has an open-source alternative called Open-Vas that offers similar features to Nessus.
John the Ripper

Passwords are still the de-facto standard of authentication in most systems. Even if you successfully get into a server or a database you will have to decrypt the password to gain privilege escalation.
John the Ripper is a simple tool used for cracking passwords. It is a super-fast password cracker with support for custom wordlists. It can run against most types of encryption methods like MD5 and SHA.
Aircrack-ng

Aircrack-ng is a set of tools that help you to work with wireless networks. Aircrack comprises of tools that can capture wireless networks, crack WPA keys, inject packets, etc.
A few tools in Aircrack-ng suite include:
- airodump — Captures packets
- aireplay — Packet injection
- aircrack — Crack WEP and WPA
- airdecap — Decrypt WEP and WPA
Aircrack contains excellent algorithms for cracking WiFi passwords and to capture wireless traffic. It can also decrypt encrypted packets, making it a complete suite of tools for wireless penetration testing. In short, you can use Aircrack for monitoring, attacking, and debugging all types of wireless networks.






Comments
Post a Comment